How To Treat Your Wounds?
Many of us think having a scrape or a wound is not a big deal. However, if the skin ruptures, the risk of infection increases. So this blog will help you to treat your damages in a way that reduces the chance of disease. Be cautious; if you have a severe wound or an infection, seek immediate medical help.
What are the types of wounds?
The wounds are generally categorized according to the extent of the injury and the type of injury. So let’s have a slight look at them one by one.
Cuts: These are usually caused by sharp objects like a knife or broken glass pieces in the kitchen. You may also have minor scratches from shrubby plants while pruning. Their treatment is simple and can be done at home.
Lacerations are deep cuts or skin tears and usually have uneven edges.
Grazes or abrasions: The surface injuries of the upper skin layer occur when damaged by friction like road rash. A person may get scrapes when he falls off a skateboard or bike, and his body strides across the ground.

Puncture wound: A keep wound caused by a sharp pointed object, like a nail that penetrates the skin or by animal biting. These injuries are profound and prone to infection but do not bleed much.
Surgical wounds: These are the cuts made during surgery and are closed with stitches.
Pressure sores or ulcers: As evident from the name, these types of scars develop mainly on the back of patients that remain immobile for a long time. Patients with diabetes are also prone to pressure sores.
Treat minor wounds at home.
Wash your hands first! Washing your hands will deter you from transmitting germs from your hands to the wound.
Press your wound using a clean bandage to prevent bleeding and promote clotting.
Raise the wounded part above your heart: if the wound is on your arm or hand, raise them above in the air. For leg or foot wounds, lay down on the bed and lift your leg by placing pillows beneath.
Rinse the wound with clean water: It will work to remove the dirt and other infection-causing agents from the skin. Avoid using alcohol or hydrogen peroxide to clean wounds; it may harm the tissues and elongate the healing process.
Use tweezers to remove embedded residue from the wound: Some particles may not go away by simple rinsing. Mark the use of tweezers to eradicate the particles embedded in the damage. Make sure to rinse the tweezers with a disinfectant, like rubbing alcohol, before using them. If you cannot remove the debris from the wound, it is better to seek medical help.
Apply antibiotic cream to stop infection: Once you notice that the wound stops bleeding, gently apply an antibiotic cream all over the wound and its surrounding skin.
Cover your wound with a bandage: If the damage is located on the flat part of your skin, apply an adhesive applied to it. Use wrapping bandages for the wounds near or on joints. Do not wrap tightly; it may hinder blood circulation.
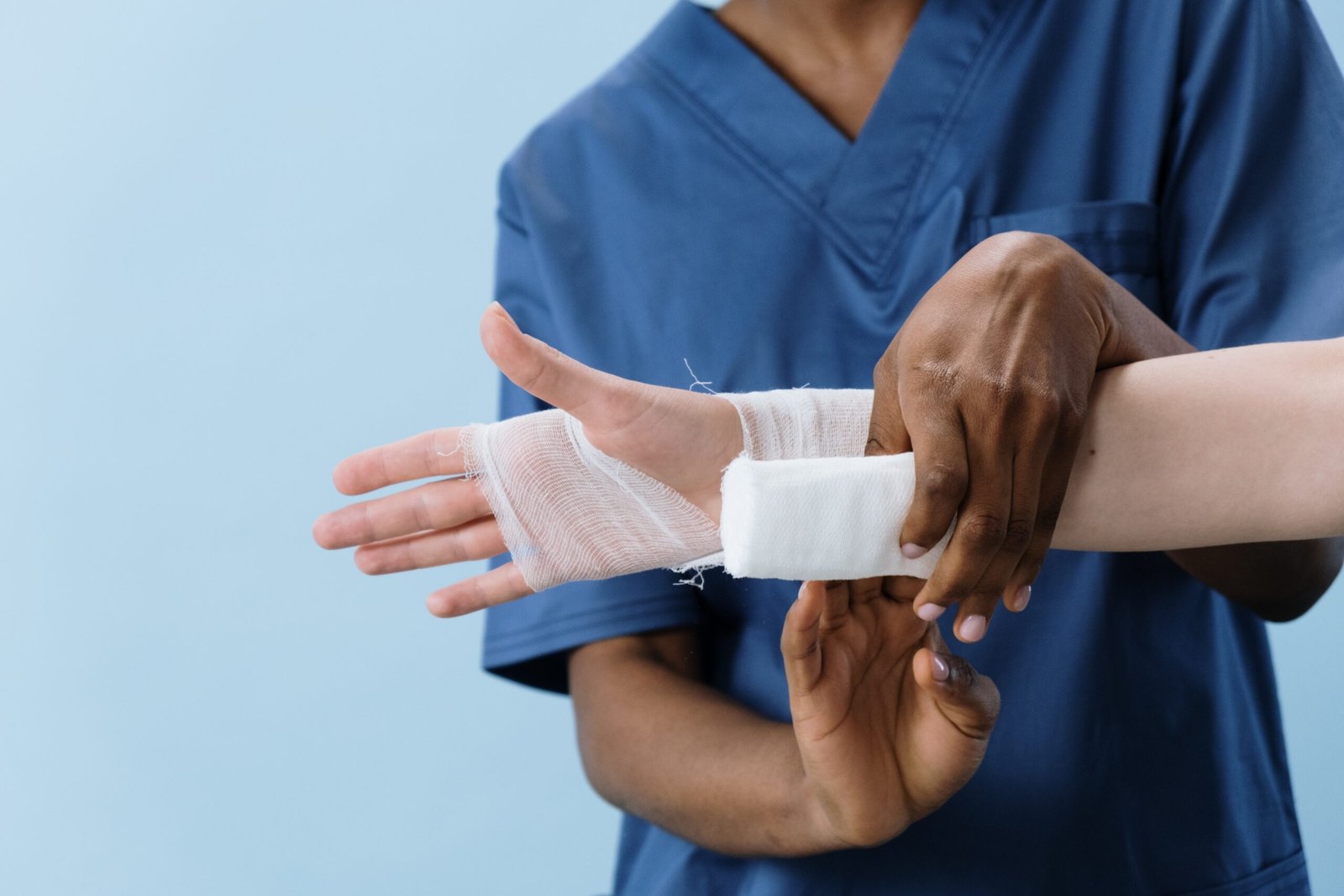
Wrap your scar with plastic while taking a bath: To keep your wound dry, wrap your wound with a waterproof bandage or use a plastic sheet to wrap your spot.
Change the dressing: Do this at least once a day or whenever the bandage becomes wet or dirty.
Keep monitoring the wound for infections.
Monitor your scar for signs like pain, pus, bleeding, redness, or fever. If you persistently have any of these symptoms, plan a visit to your healthcare provider. The doctor will prescribe antibiotics to help your body fight off the infection.
For severe wounds, get immediate medical help.
You need professional medical care if you have a severe wound, that includes,
- Cut arteries
- Deep cuts
- Bone or tendon injury
- Wounds with a foreign object stuck inside
- Long jagged cuts
- Facial wounds
- Contaminated wounds
Medical treatments
There are various types of procedures that a doctor may perform to close a wound.
Stitches: The wounds above two and a half inches long are sewn using sterile thread. Don’t worry; if stitches are needed for your injury, the doctor will numb your skin with medicine first.

After 5 to 7, the doctor removes the stitches. If the wound is more comprehensive, the doctor may recommend you wait for 7 to 14 days till the wound heals. Removing your stitches by yourself is not a great idea at all. You may further damage your skin. Please let the professionals do their work.
Tissue adhesive glue: Your healthcare provider may apply skin glue as a liquid or paste to the edges of the wound. It takes only a few minutes to set. However, the adhesive usually forms a scab that peels or falls off in 5 to 10 days.
Butterfly stitches: These are sticky strips that hold the wound closed. The doctor will remove them after the wound heals. Do not try to remove them yourself.
Antibiotics for infected wounds: If your wound is infected, the doctor will clean the wound and recommend you an antibiotic medication to eliminate the infection.
Get a tetanus shot: Get a tetanus shot if the wound is deep or dirty. There is no cure for tetanus, so the best prevention is to get it. If you have had a tetanus shot in five years, skip this step.
For non-healing wounds, visit a wound care center.
- The severe wounds started healing after two weeks and healed within six weeks. If you have an injury that is not healed yet, visit a wound care center.
- The doctors will check your wound and educate you on how to clean your wound correctly to speed up the healing process.
- If you have a low blood supply to your wound, they will teach you exercises to maintain a healthy blood flow to the injury.
- Sometimes the wounds may not heal properly because of the buildup of dead tissues. The doctor will remove the dead tissue by applying chemicals that dissolve dead tissue or using wet-to-dry dressings that dry on the wound and absorb dead tissue.
The howtothing.net article on How to treat a minor cut and How to treat an open wound provides similar details on how to provide first aid treatment to yourself at home and when to seek professional treatment.
Medical Disclaimer
The content of this blog post is not aimed at substituting for professional medical advice or treatment. It’s always appreciated to contact your healthcare provider before starting, shifting, or halting any health treatment.
